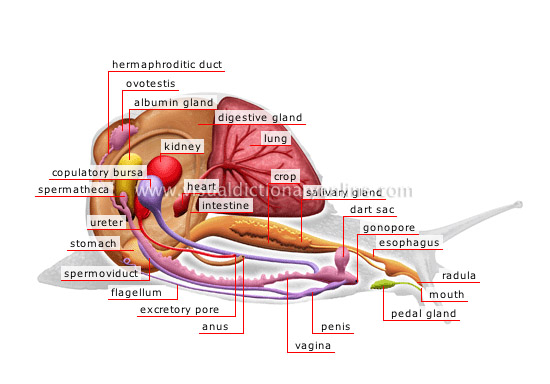
anatomy of a snail
ovotestis 
Genital gland located at the apex of the shell ensuring production of sperm and eggs; the snail has both male and female organs.
hermaphroditic duct 
Channel into which the ovotestis and albumen gland open; it separates into a sperm duct and an egg duct that remain, nonetheless, conjoined.
albumin gland 
Organ opening into the hermaphroditic duct and secreting a viscous substance, which surrounds the fertilized ovum and contributes to the development of the egg.
copulatory bursa 
Sac where sperm accumulate before entering the spermatheca.
penis 
Male organ of copulation, internal when at rest; it is located on the ventral face of the foot, lateral to the vagina.
esophagus 
Canal in the anterior part of the digestive tract; it carries food to the crop.
gonopore 
Opening common to the penis and the vagina and located at the side of the head; it allows copulation and entry of the sperm into the copulatory bursa.
pedal gland 
Organ of the foot located near the mouth; it secretes an adhesive substance that allows the snail to crawl.
radula 
Tongue bearing numerous small corneous teeth allowing the snail to grasp and tear up food before ingesting it.
mouth 
Anterior cavity of the digestive tract having a jaw and a rough tongue (radula) to graze on plants.
dart sac 
Calcareous part located inside the vagina containing the dart with which snails sting one another to achieve arousal before copulation.
crop 
Large sac located beyond the esophagus, where food is held before being digested in the stomach.
salivary gland 
Organ located in the buccal cavity; it secretes saliva and enables especially the digestion of food.
lung 
Pouch formed of a network of blood vessels inside the shell; it ensures respiration and communicates with the outside through an orifice.
heart 
Muscular organ helping blood to circulate.
digestive gland 
Organ producing a secretion that contributes to digestion.
intestine 
Section of the digestive tract between the stomach and the anus where absorption of nutrients is carried out and waste is transformed into fecal matter.
spermatheca 
Pouch discharging into the vagina and housing the sperm used to fertilize the eggs.
kidney 
Organ secreting urine; it eliminates toxic substances from the body.
stomach 
Dilated section of the digestive tract preceding the intestine; it receives food to be digested.
ureter 
Long canal originating in the kidney and carrying urine to the excretory orifice.
spermoviduct 
Male genital duct carrying sperm toward the penis.
flagellum 
Movable filament appended to the penis allowing sperm to move about during copulation.
excretory pore 
Terminal opening of the ureter allowing urine to be evacuated.
anus 
Terminal orifice of the digestive tract enabling ejection of fecal matter.
vagina 
Female organ of copulation located on the ventral surface of the foot, lateral to the penis.