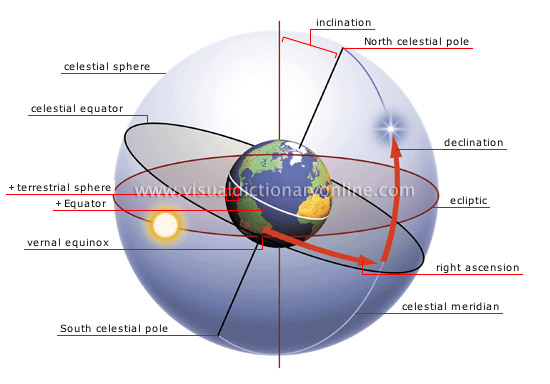
celestial coordinate system
Imaginary horizontal and vertical lines used to describe the position of an object on the celestial sphere.
North celestial pole 
Projection of the North terrestrial pole onto the celestial sphere.
declination 
One of two coordinates used to locate a celestial body on the celestial sphere; similar to terrestrial latitude.
ecliptic 
Projection of the Sun’s apparent annual path onto the celestial sphere.
right ascension 
One of two coordinates used to locate a celestial body on the celestial sphere; similar to terrestrial longitude.
celestial meridian 
Projection of a terrestrial meridian onto the celestial sphere.
celestial sphere 
Imaginary sphere where celestial bodies are observed and positioned.
celestial equator 
Projection of the terrestrial Equator onto the celestial sphere; serves as the point of origin for declinations.
terrestrial sphere 
Shape of Earth whose coordinates are projected onto the celestial sphere.
vernal equinox 
Point at which the ecliptic and the celestial equator intersect; serves as the point of origin for right ascensions.
South celestial pole 
Projection of the South terrestrial pole onto the celestial sphere.
Equator 
Imaginary circle surrounding Earth at its widest circumference, dividing it into two hemispheres: the Northern hemisphere and the Southern hemisphere.
inclination 
Angle formed between an imaginary line connecting the terrestrial poles and an imaginary line perpendicular to the ecliptic.