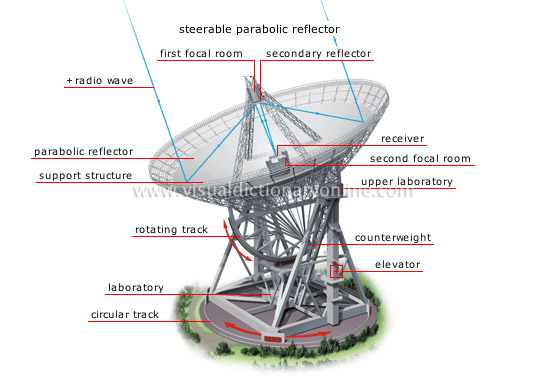
radio telescope
Instrument used to capture, concentrate and analyze radio waves emanating from a celestial body or a region of the celestial sphere.
steerable parabolic reflector 
Type of adjustable radio telescope in the shape of a saucer; its power depends on its diameter.
second focal room 
Secondary focus of the radio telescope that houses the radio receiver; used more often than the first focal room.
parabolic reflector 
A surface often composed of fine wire-mesh that collects radio waves and causes them to converge on a single point.
first focal room 
Observation capsule used on occasion; located in the prime focus of the radio telescope.
secondary reflector 
Receives waves reflected by the parabolic reflector and directs them toward the receiver.
laboratory 
Area where astronomers analyze the digital signal to obtain information.
rotating track 
Rail making it possible to turn the radio telescope vertically so as to point it toward a given region of the sky.
support structure 
Structural element on the rim that prevents the parabolic reflector from becoming deformed.
radio wave 
Invisible electromagnetic waves emitted by celestial bodies and collected on Earth using a radio telescope.
circular track 
Rail making it possible to turn the radio telescope horizontally so as to point it toward a given region of the sky.
elevator 
counterweight 
Weight equal to that of the parabolic reflector; makes it possible to balance the whole.
upper laboratory 
Area where the electrical signal is filtered, digitized and transmitted to the laboratory.
receiver 
Device that amplifies waves before they are converted into an electrical signal.