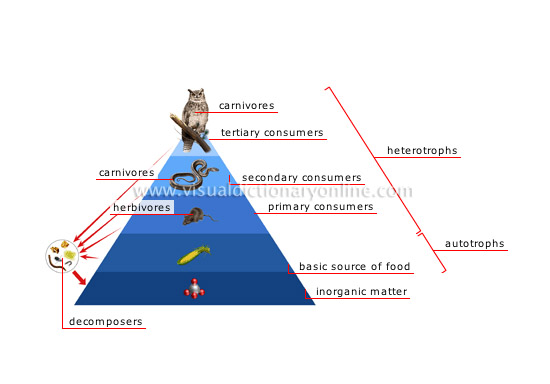
food chain
Order of the relationships of predation and dependence among living organisms.
autotrophs 
Organisms capable of making their own food from inorganic matter and solar energy.
inorganic matter 
Matter of mineral origin, converted by bacteria; the nitrogen, salts and water it retains serve as food for plants.
heterotrophs 
Organisms that feed on organic matter that is already broken down, since they are unable to feed on mineral compounds.
decomposers 
Organisms that break down organic matter (dead animals, excrement, plant residue) into mineral components that can be reused by plants.
secondary consumers 
Carnivores that feed on herbivores.
tertiary consumers 
Carnivores that feed on other carnivores.
carnivores 
Animals that feed mainly on meat.
herbivores 
Animals that feed on plants.
primary consumers 
They feed on autotrophic organisms and are therefore usually herbivores.
basic source of food 
Vegetables are at the base of the food chain for all other consumers; they are eaten raw or converted into meat by animals.
carnivores 
Animals that feed mainly on meat.