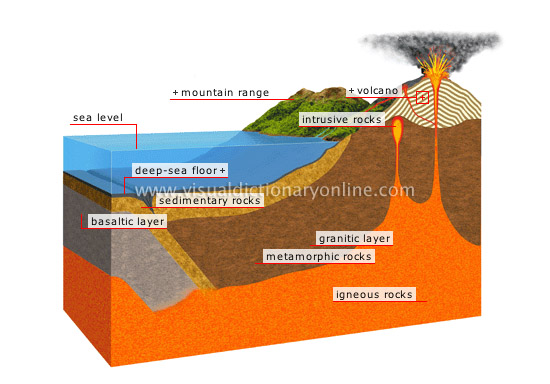
section of the Earth’s crust
The Earth’s crust, continental and oceanic, is composed mainly of sedimentary, metamorphic and igneous rock.
sedimentary rocks 
Rocks formed by the accumulation, compaction and cementation of fragments of eroded rock and debris left by living organisms.
granitic layer 
Layer of granite that gives the continents their essential form.
basaltic layer 
Layer of basalt, a rock denser than granite, that forms the deep-sea floor and is covered with various types of debris.
deep-sea floor 
Part of the Earth’s surface beneath the seas and the oceans; its topography is highly variable.
sea level 
Average height of seawater observed for a given time (day, month, year); it is used as a reference point to define coastal features and measure land elevations.
intrusive rocks 
Igneous rocks that have risen close to the Earth’s surface.
mountain range 
A row of elevated connected landforms characterized by high summits and deep valleys.
volcano 
Landform built up as lava and ash are ejected from the upper mantle during successive eruptions, accumulating and solidifying on the surface.
igneous rocks 
Rock formed from molten magma that has cooled and solidified inside the Earth; also called magmatic rock.