underground mine
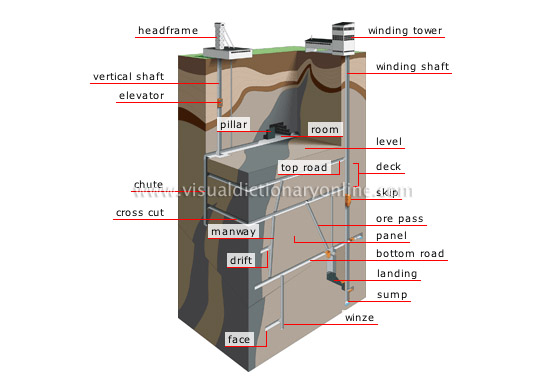
Property in which excavations are carried out to extract deeply embedded (between 30 and 11,500 ft) coal for industrial mining.
elevator 
Power lift fitted with a cab that transports coal or miners between the various levels.
room 
Cavity that remains after the ore is extracted; pillars support its roof.
sump 
Bottom of the shaft in which water runoff accumulates inside the mine before being pumped to the surface.
deck 
Extraction layer between two levels; mining is usually done in stages and in descending order.
level 
The horizontal passageways that branch off from the shaft at the same depth; they are usually at regular intervals.
drift 
Passageway dug horizontally along the grade line of the ore seam; it can also be dug into the ore vertically.
face 
Opening that is dug laterally into the rock as coal is extracted.
cross cut 
Horizontal passageway that cuts through the ore bed perpendicularly; it provides communication between the passageways and helps to ventilate the mine.
chute 
Vertical or inclined passageway through which ore, equipment, personnel and air move from one level of the mine to the other.
winze 
Vertical or inclined passageway that connects two levels; it is dug downward from inside the mine and not from the surface.
manway 
Passageway allowing workers to move around in the mine.
landing 
Landing located around a shaft on each level; coal is collected here before being moved to the surface.
panel 
Unit of rock that is being mined; it is contained between vertical and horizontal planes and is demarcated by various passageways.
ore pass 
Inclined route that takes coal to a lower level; coal that falls on the mine floor is usually crushed before being brought to the surface.
skip 
Elevator consisting of a skip bucket that is activated by a hoist; it is used to bring coal and people to the surface.
top road 
Horizontal passageway that serves the highest level of a panel.
pillar 
Mass of ore that is left unmined at regular intervals in an excavation (chamber); it provides stability for the upper layers.
winding shaft 
Shaft that is dug vertically into the ground; coal is removed from the mine through it using hoisting machinery.
winding tower 
Building that houses the shaft’s hoisting equipment (including motors and hoisting cables); it provides communication between the surface and the mine galleries.
vertical shaft 
Shaft that is dug perpendicular to the surface; it serves various levels and is used mainly to transport personnel, equipment and ore.
bottom road 
Horizontal passageway that serves the base of a panel.
headframe 
Opening at the top of the shaft that connects the aboveground facilities (including ventilation fans and hoists) to the underground areas being mined.