production of electricity from solar energy
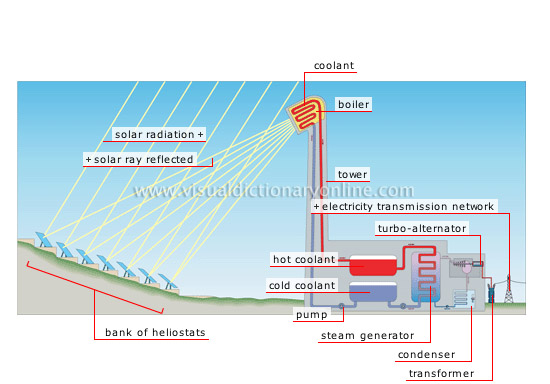
Heating the coolant directly with solar rays turns water into steam, which then turns the turbo-alternator to produce electricity.
turbo-alternator 
Device that uses steam to convert the mechanical force generated by the rotation of the turbine into electricity.
electricity transmission network 
Electricity is carried over vast distances by a network of cables that extends from the power plant to consumers.
condenser 
Circuit that cools the steam from the turbine and condenses it into water, which is reintroduced into the steam generator.
steam generator 
Device that uses heat to convert water into steam to activate the turbo-alternator.
cold coolant 
After releasing its heat to the steam generator, the cold coolant returns to the boiler.
hot coolant 
The coolant extracts heat from the boiler and carries it to the steam generator and turbine.
pump 
Device that ensures that the cold coolant liquid flows to the boiler.
bank of heliostats 
Heliostats: remote-controlled adjustable mirrors that follow the Sun’s trajectory and concentrate solar radiation toward the boiler at the top of the tower.
solar radiation 
The Sun emits waves in the form of luminous radiation (41% visible light, 52% infrared light and 7% ultraviolet light).
solar ray reflected 
Solar rays trapped by heliostats are sent to the boiler.
coolant 
Fluid (e.g., a mixture of melted salts) that traps the heat from concentrated solar radiation and carries it to the turbine.
tower 
Structure atop which the boiler sits and collects luminous energy; it can reach 325 ft in height.
boiler 
Enclosure in which the concentrated heat from the Sun’s rays raises the temperature of the coolant.