sensory impulse
Electrical signal propagated along the nerve fibers (axons) enabling the nerve cells to communicate and to transmit messages within the organism.
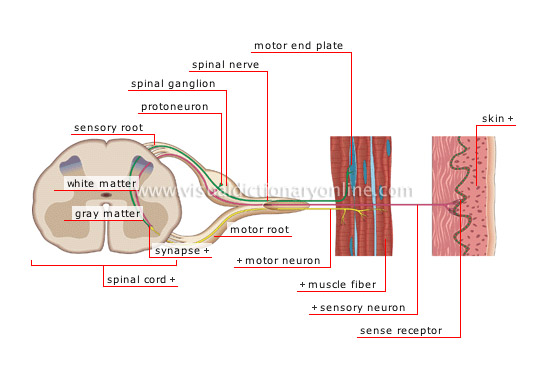
motor end plate 
Contact zone between the axonal end of the motor neuron and the muscle fiber that causes muscle movement.
white matter 
Section of the spinal cord made up of nerve fibers (axons) and surrounding the gray matter.
gray matter 
Central part of the spinal cord primarily made of the cell bodies of neurons.
muscle fiber 
Component tissue of the muscle; it contracts in response to a nerve impulse from the central nervous system.
sensory neuron 
Neuron transmitting information gathered by sensory receptors to the central nervous system.
sense receptor 
Peripheral terminal of the sensory neuron receiving a stimulus (touch, noise or other) and transmitting it to the spinal cord in the form of nerve impulses.
skin 
The body’s outer protective casing whose internal layer (dermis) is rich in veins and nerves.
spinal cord 
Part of the central nervous system located in the spinal column; it receives and transmits nerve information and initiates reflex actions.
synapse 
Contact zone between two neurons through which nerve impulses are transmitted.
motor root 
Bundle of motor nerve fibers (axons) communicating information from the spinal cord to the periphery of the body, especially the muscles.
motor neuron 
Neuron conducting nerve impulses from the central nervous system to the peripheral organs, such as the muscles.
spinal nerve 
Nerve formed by the union of the sensory and motor roots; it communicates nerve messages between the spinal cord and the various parts of the organism.
protoneuron 
First neuron of the sensory tract; it transmits information from a sensory organ to the spinal cord.
spinal ganglion 
Bulge of the posterior sensory root of the spinal nerve; it encloses the cell bodies of the neuron sensors.
sensory root 
Bundle of sensory nerve fibers (axons) communicating information from the periphery of the body to the spinal cord.