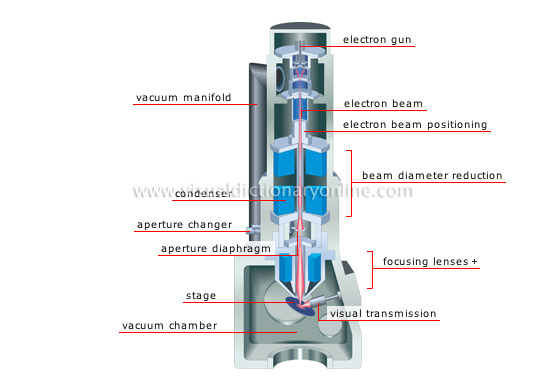
cross section of an electron microscope
Electron microscope: it uses an electron beam (as opposed to light) to provide magnification that is markedly superior to that of an optical microscope.
stage 
Adjustable metal plate (stage) on which the specimen is mounted in order to study it.
aperture diaphragm 
Device with an opening whose diameter can be changed to narrow or widen the diameter of the electron beam.
aperture changer 
Device that adjusts the diaphragm opening in order to change the diameter of the beam.
condenser 
System of magnetic lenses (electromagnets producing a magnetic field when excited by an electric current) that concentrates the beam onto the specimen under study.
vacuum manifold 
Conduit connected to a pump that creates enough of a vacuum in the microscope that it can function.
electron gun 
Device that usually consists of a tungsten filament that is heated to produce an intense electron beam, which illuminates the specimen.
vacuum chamber 
Part of the microscope in which pressure can be reduced so that the electrons can move.
visual transmission 
The electron beam explores the surface of the specimen, which in turn emits electrons to form a point-by-point image on the screen.
focusing lenses 
System of magnetic lenses (electromagnets) that concentrate the electron beam on one spot on the specimen.
beam diameter reduction 
The two lenses of the condenser cause the divergent electron beam emitted by the gun to converge.
electron beam positioning 
Control that positions the electron beam along the optical axis so that it reaches the specimen.
electron beam 
Set of negatively charged particles that propagate toward the specimen.