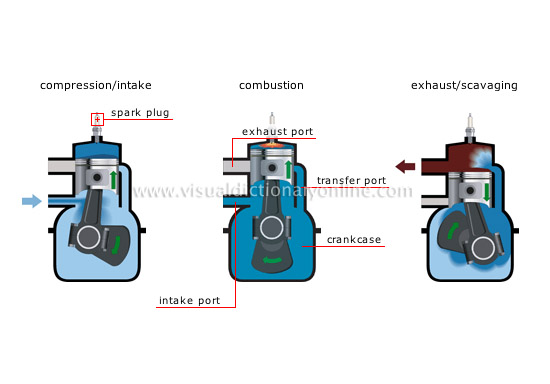
two-stroke-cycle engine cycle
Two-stroke engine: combustion engine whose cycle (intake, compression, combustion and exhaust) requires one up-and-down movement of the piston.
exhaust/scavaging 
Second stroke during which the piston is pushed back by the expansion of the burned gases, which are then expelled and replaced by the mixture coming from the crankcase.
combustion 
End of the first stroke during which a spark ignites the air/fuel mixture.
intake port 
Conduit through which the air/fuel mixture enters the crankcase.
exhaust port 
Conduit through which the burned gases are expelled from the combustion chamber.
crankcase 
Sealed enclosure where the air/fuel mixture enters and the piston/connecting rod moves.
transfer port 
Conduit conducting the air/fuel mixture from the crankcase to the cylinder.
compression/intake 
Beginning of the first stroke during which the piston moves up, drawing the air/fuel mixture into the crankcase and compressing the mixture in the cylinder.
spark plug 
Electric device whose two electrodes produce the spark necessary to ignite the air/fuel mixture in the cylinder.