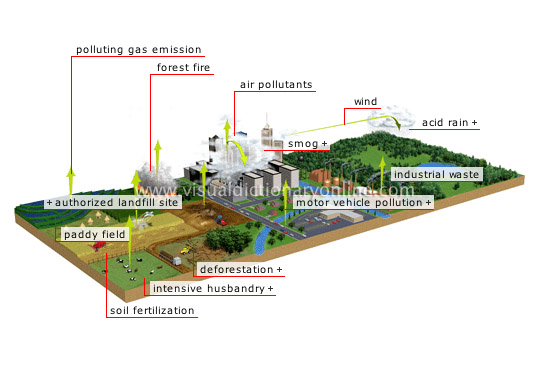
air pollution
The presence in the atmosphere of large quantities of particles or gases produced by human activity; these are harmful to both animal and plant life.
paddy field 
Paddy fields release considerable quantities of methane.
soil fertilization 
Nitrogen fertilizers used to fertilize the soil also release nitrogen oxides.
intensive husbandry 
Bacteria involved in the digestion of ruminants also trigger the emission of methane into the air.
deforestation 
Large-scale deforestation leads to increased carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere since plants alone absorb and retain this gas.
motor vehicle pollution 
Motor vehicle exhaust contains carbon particles, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide and hydrocarbons.
industrial waste 
Depending on their activity, industries emit a great variety of pollutants such as nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, ozone, heavy metals and hydrocarbons.
acid rain 
Rain that contains an unusually high concentration of sulfuric acid and nitric acid.
wind 
Polluted clouds are carried by the wind, sometimes traveling thousands of miles; their pollutants then fall in the form of acid rain.
smog 
Harmful haze resulting from the presence of polluting gases; it forms over cities under specific meteorological conditions.
air pollutants 
The principal air pollutants are sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons, methane and carbon dioxide.
forest fire 
Forest fires and brush fires release carbon monoxide, methane and nitrogen oxides.
authorized landfill site 
In waste landfill sites, decomposing organic matter produces methane.
polluting gas emission 
Most polluting gases are present in the atmosphere in minuscule quantities, but human activity increases their concentration.