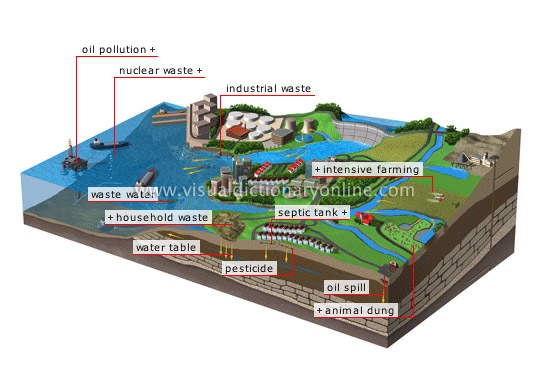
water pollution
The cycle of the Earth’s waters is continuous, carrying and spreading pollutants introduced by human activity all around the planet.
El Diccionario Visual, a new valuable resource to learn Spanish. Includes 17 all-around themes to explore, including the human body, sciences and food.
intensive farming 
To achieve maximum production, intensive farming uses chemical fertilizers responsible for various forms of air and water pollution.
animal dung 
Animal dung introduces large quantities of nitrate into the soil; the nitrate then filters into the water table.
oil spill 
Certain underground gas tanks leak, discharging hydrocarbons into the water table.
pesticide 
Pesticide residue is found in the water table and in watercourses; it makes water unfit for consumption.
septic tank 
Wastewater leakage from a dwelling’s underground tank contaminates the water table.
water table 
Vast expanse of underground water fed by rainwater filtering through the earth; it supplies springs and can be collected in wells.
household waste 
Burying household waste without taking any particular precautionary measures leads to contamination of the water table.
waste water 
Untreated, it contains organic matter (e.g., bacteria, viruses) and potentially pathogenic substances that cause infection and promote the growth of algae.
oil pollution 
Pollution caused by leaks from refineries and offshore drilling platforms, by ships emptying their fuel tanks at sea and by oil spills.
nuclear waste 
Radioactive nuclear waste was once immersed at the bottom of the ocean; it has a life span of up to 1,000 years.
industrial waste 
Industrial waste is highly variable; its principal components are lead, mercury, cadmium, hydrocarbons and acid deposits.