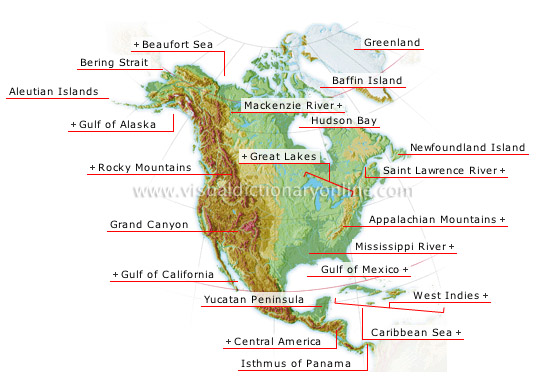
North America
The Appalachians constitute the principal relief on the eastern part of the continent, while in the west, high mountain chains (the Rocky Mountains and the Sierra Madre) follow the coast from Alaska to Mexico.
Grand Canyon 
The longest gorge in the world (220 mi); the Colorado River flows through it.
Gulf of California 
Separates the Baja California peninsula from the continent.
Gulf of Mexico 
Part of the Atlantic located between the U.S., Mexico and Cuba.
Yucatan Peninsula 
Vast plateau characterized by aridity in the northwest and abundant precipitation in the south, where a dense forest grows.
Central America 
Extends from the Isthmus of Tehuantepec in Mexico to the Isthmus of Panama.
Isthmus of Panama 
Cut by a canal with locks that is 50 mi long. The Panama Canal opened in 1914 allowing maritime traffic to travel between the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean.
Caribbean Sea 
Body of water (1.1 million mi2) located between Central America and the northern portion of South America.
West Indies 
Archipelago that includes more than 700 islands, including the Greater Antilles in the north (Cuba, Haiti, Jamaica, Puerto Rico) and the Lesser Antilles in the east.
Mississippi River 
The Mississippi (2,350 mi) drainage basin covers the entire area between the Rocky Mountains and the Appalachians.
Appalachian Mountains 
Old massif extending over 1,200 mi from the Canadian border to Alabama; its highest peak is Mount Mitchell (6,684 feet).
Saint Lawrence River 
River (over 680 mi) that drains southeastern Canada and empties into the Atlantic Ocean.
Newfoundland Island 
Great Lakes 
These five lakes constitute the world’s largest reserve of fresh surface water (95,000 mi2).
Aleutian Islands 
Archipelago that is an extension of Alaska; it is composed of 150 islands and islets stretching over more than 1,000 mi.
Gulf of Alaska 
Northeast part of the Pacific Ocean, bordering Alaska.
Greenland 
Second largest island in the world (over 770,000 mi2) after Australia.
Baffin Island 
Island in the Arctic Archipelago; the Baffin Sea separates it from Greenland.
Hudson Bay 
Vast gulf that opens onto the Atlantic Ocean through the Hudson Strait; the bay is frozen seven months a year.
Mackenzie River 
Canada’s longest river (2,635 mi).
Beaufort Sea 
Part of the Arctic Ocean between Alaska and the Arctic Archipelago.
Bering Strait 
Some 62 mi wide, it connects the Pacific Ocean to the Arctic Ocean.
Rocky Mountains 
Eastern margin of the western cordilleras, extending from Alaska to Mexico.