planisphere
Map depicting the Earth’s two hemispheres.
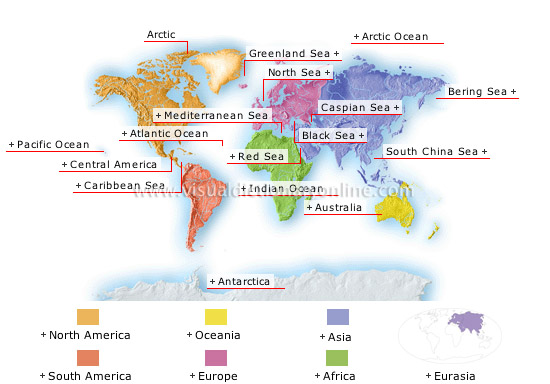
Pacific Ocean 
The world’s largest ocean (69 million mi2), the Pacific covers 30% of the Earth’s surface, more than all of the continents put together.
Central America 
Extends from the Isthmus of Tehuantepec in Mexico to the Isthmus of Panama.
Caribbean Sea 
Body of water (1.1 million mi2) located between Central America and the northern portion of South America.
Atlantic Ocean 
The world’s second largest ocean (36 million mi2); it covers 20% of the Earth’s surface.
Antarctica 
The only uninhabited continent (5 million mi2), located inside the south polar circle; 98% of its surface is covered with an ice cap. Antarctica holds 90% of the Earth’s freshwater reserves.
Red Sea 
Gulf (165,000 mi2) located between Africa and the Arabian Peninsula; it connects to the Mediterranean through the Suez Canal.
Australia 
The world’s largest island (3 million mi2) is sparsely inhabited in spite of its size; because of its isolation, Australia’s wildlife is unique.
Indian Ocean 
Relatively small ocean (29 million mi2) located between Africa, Asia and Australia; it has high water temperatures and is dotted with numerous islands.
Arctic Ocean 
The smallest of the oceans (5.8 million mi2), bordered by the northern coasts of Asia, America and Europe; it is largely covered with pack ice.
South China Sea 
Southern part of the China Sea bordering the entire southeast coast of Asia as well as Borneo, the Philippines and Taiwan.
Bering Sea 
Northern part of the Pacific between Kamchatka (in Asia) and Alaska; it is deepest in its southern portion.
Caspian Sea 
The world’s largest lake (140,000 mi2), located between Europe and Asia; it has no link to an ocean and is diminishing in size.
Black Sea 
Inland sea (162,000 mi2) between Eastern Europe and Asia; it opens into the Mediterranean through two straits, the Dardanelles and the Bosporus.
Mediterranean Sea 
One of the largest inland seas in the world (965,000 mi2); it lies between Europe, Africa and Asia and connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the Strait of Gibraltar.
Greenland Sea 
Sea (465,000 mi2) in the North Atlantic; it is bordered by the coast of Greenland.
North Sea 
Relatively shallow sea (220,000 mi2) in the North Atlantic and bordered by the coasts of Europe; some major European ports are located along its estuaries.
Arctic 
Vast region inside the north polar circle; it includes the Arctic Ocean and the lands bordering it.
Eurasia 
Composed of Europe and Asia, Eurasia represents about 39% of the world’s land; it forms a true continent that geographers have distinguished for historical and ethnographic reasons.
Africa 
Continent that represents about 20% of the world’s land; two-thirds of its surface lies north of the Equator. Characterized by very hot climates, Mediterranean in the north and south, tropical and arid elsewhere.
Asia 
The largest and most populous continent, Asia represents 32% of the world’s land; it is dominated by imposing mountain ranges.
Europe 
Western extremity of the vast Eurasian continent that, by convention, is separated from Asia by the Ural Mountains; it covers a relatively small area.
Oceania 
Continent that represents 6% of the world’s land and features a great many islands in the Pacific and Indian oceans; Australia is its true continent.
South America 
Represents 12% of the world’s land; linked to North America by Central America; it includes the Andes in the west and plains and plateaus in east and central regions.
North America 
Its area (9.3 million mi2) represents about 16% of the world’s land; the Central American isthmus is an extension of North America.