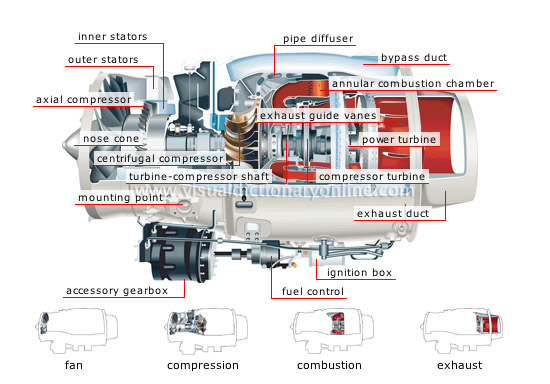
turbofan engine
Jet engine with a fan and two airflows; one airflow passes through the combustion chamber and the other bypasses it.
exhaust duct 
Opening through which the exhaust gases are evacuated; the duct is usually cone-shaped in order to narrow the gas flow, thus increasing thrust.
power turbine 
Turbine that is driven by the gases expelled by the combustion chamber; it drives the axial compressor and the fan. It is independent of the compressor turbine.
ignition box 
Device that produces the electric pulses supplying the system that sets off combustion.
compressor turbine 
Turbine that is activated by the gas produced in the combustion chamber; it drives the centrifugal compressor and the accessories.
fuel control 
Device measuring the amount of fuel injected into the combustion chamber.
accessory gearbox 
Mechanism that drives various accessories such as the alternator and the hydraulic, fuel and oil pumps.
mounting point 
Part where the engine is mounted on the aircraft.
nose cone 
Part located on the tip of the fan axle that creates an aerodynamic airflow into the fan blades.
exhaust guide vanes 
Protruding parts directing the exhaust gases straight out.
bypass duct 
Channel that conducts some of the air sucked in by the fan, which contributes to the engine’s thrust.
annular combustion chamber 
Enclosure consisting of two concentric hydraulic cylinders that surrounds the turbine-compressor shaft and where combustion occurs.
turbine-compressor shaft 
Axle transmitting the turbine’s rotational movement to the compressors.
pipe diffuser 
Conduit with several exit orifices that connects the centrifugal compressor to the combustion chamber; its purpose is to direct the flow and slow down the airflow to increase its pressure.
centrifugal compressor 
Engine components that use centrifugal force to compress air and expel it at very high speed to the combustion chamber by the pipe diffuser.
inner stators 
Set of fixed blades that corrects the airflow that is deflected as it passes through the blades of the axial compressor.
outer stators 
Set of fixed blades that corrects the airflow that is deflected as it passes through the fan.
axial compressor 
Engine component in which air is highly compressed by a set of small fan blades to increase the engine’s output and reduce fuel consumption.
exhaust 
Phase during which the air expands and produces a thrust that activates the turbines and propels the turbofan engine.
combustion 
Phase during which the compressed air enters the combustion chamber, where it is mixed with fuel and ignited.
compression 
Phase during which some of the air flowing through the engine is compressed before it enters the combustion chamber.
fan 
Blower sucking air into the turbofan engine.