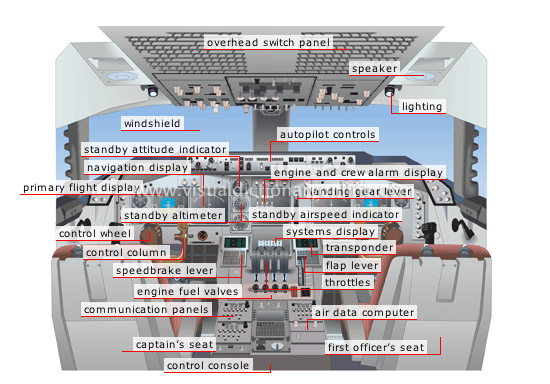
flight deck
Compartment that contains navigation equipment and controls and from which the crew pilots the aircraft.
air data computer 
Computer that calculates the flight parameters (speed, altitude and course).
transponder 
Instruments that, with the autopilot, control the engine power and guide the aircraft on its course.
first officer’s seat 
Right seat occupied by the copilot, who is second in command.
flap lever 
Control stick that activates the wing slats and the trailing edge flaps.
control console 
Component located between the two seats that contains part of the instrumentation.
engine fuel valves 
Knobs for opening and shutting the fuel supply to the engines.
communication panels 
Panel for selecting radio frequencies on which pilots can send or receive.
throttles 
Control levers for the engines; they regulate speed and thrust.
captain’s seat 
Left seat occupied by the pilot, who is in charge of the flight and the crew.
systems display 
Screen that controls various systems, such as air pressure and the electric and hydraulic circuits.
speedbrake lever 
Command stick that releases the wing flaps to brake the aircraft immediately after landing.
control wheel 
Lever that activates the control column from back to front and from side to side.
control column 
Steering component that causes an aircraft to bank to the left or to the right and to ascend or descend.
primary flight display 
Screen that shows the main parameters necessary for piloting (aircraft’s position in relation to the horizon, altitude and course).
navigation display 
Screen that shows the aircraft’s position and flight plan and weather conditions.
standby altimeter 
Instrument that shows the vertical distance between the aircraft and the ground; it is used in the event the flight display fails.
standby airspeed indicator 
Instrument that shows the aircraft’s speed; it is used in the event the flight display fails.
standby attitude indicator 
Screen that shows the aircraft’s position in relation to the horizon; it is used in the event the flight display fails.
windshield 
Highly durable pane made of glass and plastic that provides good visibility.
engine and crew alarm display 
Screen that controls the engines and displays alarm signals in the event of system failure.
autopilot controls 
Device that enables the aircraft to be piloted and kept on course automatically.
landing gear lever 
Control for lowering and raising the landing gear.
overhead switch panel 
Panel made up of the switches that cut the hydraulic, electric and fuel circuits.
lighting 
Device that diffuses light over a shelf on which the pilots place navigation charts.
speaker 
Integrated device that relays audible messages such as alarms to the pilots.